Sinai Peninsula | Red Sea
The Sinai Peninsula
nicknamed the land of turquoise, is a triangular desert peninsula located in western Asia, in the northeastern part of the Arab Republic of Egypt, and is the only part of Egypt that geographically follows the continent of Asia, with an area of about 60,088 square kilometers, representing 6% of the total area of Egypt, bordered to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, to the West by the Gulf of Suez and the Suez Canal, to the East by historic Palestine (Gaza Strip and Israel), the Gulf of Aqaba, and to the South by the Red Sea, and it is considered the link between the continents of Africa and Asia, the population of the Sinai has about one million four hundred thousand inhabitants according to statistics in 2013.
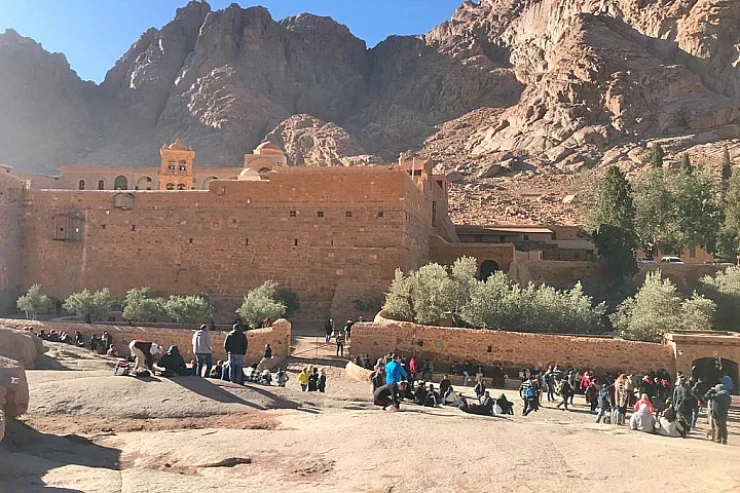
The Sinai Peninsula is divided administratively into North Sinai governorate, south Sinai governorate, Port Said governorate's Port-Fouad city, the center and city of Al-Qantara east of Ismailia governorate, and Al-Janayen neighborhood of Suez governorate, and includes among its many distinctive landmarks, as there are many tourist resorts, nature reserves and religious shrines, most notably Sharm el-Sheikh, Dahab, Ras Sidr, Taba, Nuweiba, Ras Mohammed Reserve, Nabq Reserve, Taba Reserve, St. Catherine's monastery, Musa bath, Pharaoh's bath, and Mount Musa, which the mountain on which the Prophet Moses spoke to his Lord and received the Ten Commandments, according to the Abrahamic religions.There is no clear origin for the word "Sinai", some have stated The meaning of "stone" was given to Sinai because of its many mountains, while others mentioned that its name in the ancient hieroglyphs was "tushrit", i.e. the land of the mountains and the open, and was known in the Torah as "Horeb", i.e. desolation. But it is agreed that the name Sinai, which was given to the southern part of Sinai, and the ancient Sinai monuments indicate the existence of an ancient war Road, The Horus road, and this road started from Farma to Al-Arish, which is now located in the qatiya area.the Sinai land has witnessed many historical events, most notably the First Crusade, the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, and Sinai has witnessed long stages of the Arab-Israeli conflict, the most important of which are the triple aggression of 1956, the June war of 1967, and the October War of 1973.
There is a dispute among historians about the origin of the word "Sinai", some have stated that its meaning is "stone" because of its many mountains, while others have stated that its name in the ancient hieroglyphs is "tushrit", i.e. the land of the mountains and the open, and it was known in the Torah as "Horeb", i.e. the ruin, but it is agreed that the name Sinai, which was given to the southern part of the peninsula, is derived from the name of the god "Sin", the God of the moon, according to the beliefs of ancient Babylon, where his worship spread in western Asia, including Palestine, and then the Egyptian moon, which had a great importance in Sinai, and its worship was widespread in it, and through the inscriptions of the servant's sarcophagi and the grotto, it becomes clear to us that there was no special name for Sinai, but it is referred to Sometimes by the word "biawo" i.e. mines or just " Biya "i.e." mine "and in other Egyptian sources of the New Kingdom Sinai is referred to as" Khast mafkat "and sometimes" domfkat "i.e."turquoise terraces".
Ancient times
The mystery remained shrouded in the history of ancient Sinai until Flinders Petrie in 1905 was able to discover twelve inscriptions known as "Sinai inscriptions", with an alphabet that was unknown at that time, and in some of its letters a great similarity with hieroglyphs, and these inscriptions remained a mystery until 1917, when the Egyptologist Gardner was able to decipher some of the symbols of this writing, which explained that they were nothing but Canaanite writings from the fifteenth century BC from the remnants of the ancient Canaanite civilization in Sinai.
The ruins of ancient Sinai indicate the existence of an ancient war Road, The Horus road, which cuts the Sinai, and this road started from the current Qantara, and headed north to pass on the hill of hay and then Bir Romana near Muhammadiyah, and from qatiya it goes to El Arish, and evidenced by the remains of ancient castles such as Tharu Castle, and its place is now "Abu SEIFA Hill", and the fortress "Putu" city, established by King Seti I, which is now located in the qatiya area. King smerkht, the seventh king of the first dynasty, led a campaign to the valley of the cave, home to the turquoise mines in Sinai, against the nomads there in 3200 BC, recording the news of his campaign with an inscription on a piece of rock, on which his image is considered the oldest monument in Sinai, and the Kings of that family followed him with similar campaigns and battles against the greedy and aggressors. King Djoser-one of the Kings of the Third Dynasty, nicknamed The Conqueror of the Sinai Peninsula - led a major campaign there in 2700 BC, recording his victories on a rock in the form of a fighter beating a Bedouin, and the same was repeated with the Kings of the Fourth Dynasty, nicknamed the builders of the pyramids.
He witnessed the year 1800 BC. The arrival of the father of the prophets Ibrahim (peace be upon him) to Egypt during the occupation of the Hyksos, and he married an Egyptian maid named Hagar from Al-Farma north of Qantara at the present time and gave birth to Ishmael from her, who grew up in Mecca and from his descendants came the adnanian Arabs. And in 1213 BC. The Israelites came out of Egypt during the reign of the pharaoh of Egypt, from where the prophet of God Moses (PBUH) walked to Midian-the homeland of his wife and her family, the southernmost of the present Sinai - and some believe that it is located on the western coast of the Gulf of Aqaba in the area between Taba and Dahab. When Moses walked in this direction where Mount Moses and Mount monologue are currently, it is said that Moses received the commandments and canons of the Jewish religion. The people of Moses did not respond to his desire to enter Palestine, so the wrath of Allah fell upon them and forbade them to enter it for forty years wandering in Sinai. Moses and Aaron died in Sinai during the period of wandering, where first Aaron died and was buried on Mount Hood, and then Moses died and was buried in a red Dune, which is a place close to the land of Palestine, but is currently unknown.
And in 525 BC. The Persian king Cambyses Ibn Cyrus, who came to Egypt through the Sinai, defeated the pharaoh of Egypt at that time Psamtik III, and in 333 BC. Alexander the Great invaded Egypt through Sinai and his troops were stationed in the qatiya region, either in 169 BC. The Nabataean kingdom, with its capital Petra, extended its influence from the Levant desert in the east to the Gulf of Suez in the West and from Syria in the north to Medina in the South.traces of this kingdom were found in the qatia area in the center of Bir al-Abd in North Sinai, as well as many fossils found on rocks in the Sinai Peninsula.
Middle Ages
During the Greek and Roman eras, Sinai continued to play its historical role, and trade relations arose between it and many cities that followed the pattern of Greek cities, the most famous of which was the city of Petra located in Jordan today, a fortified stone city in the valley of Moses, which was the center of the Nabataean civilization attributed to its inhabitants from the Nabataeans.there is a great dispute about the origin of the Nabataeans, and it is likely that they were of Arab origin displaced from the Hijaz, because the names of some of their kings were Arabic names such as Harith, Obadah and Malik. The Nabataeans used trade routes, mined turquoise in the valley of the grotto and copper in the valley of the monument, they visited the holy places in the mountains of Moses and serbal, and monks from Petra inhabited the monastery of St. Catherine in the early Christian era, and the Diocese of Ferran before the construction of the monastery belonged to the Diocese of Petra.
During the reign of Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab (may Allah be pleased with him), specifically on the 10th of Dhu al-Hijjah of the 18th Hijri, the Islamic army led by Amr ibn al-as crossed the Egyptian borders from the Levant and advanced towards Rafah, then Al-Arish, then Al-Farma north of present-day Qantara, where it besieged them for about two months before it fell and from there to belbis, where the rum army was defeated after besieging it for a month, and that agreed in 639 ad. The Islamic conquest encouraged some Bedouin elements in the Arabian Peninsula to migrate to Sinai and settle there, which encouraged the spread of Islam among its inhabitants, and some of these elements considered it a springboard to North Africa, some settled in Egypt while others were displaced to the Maghreb. Sinai was one of the most important human crossings during the first centuries of the Islamic conquest. These migrations that crossed the Sinai since the Islamic conquest began to increase on Sinai during the Umayyad and Abbasid eras, and then began to decrease significantly since the tulunid era, as a result of the collapse of Arab influence during the second Abbasid era, and the increasing influence of other elements such as the Persians and Turks.
During the period of the Crusades, Sinai was subjected to an attempted invasion by the Crusaders, where Baldwin I, The Crusader ruler of Jerusalem, made an incursion into the Arabah Valley to control the area south of the Dead Sea, and then in 1115 built the Shobak Fort to be a center for the Crusaders to control the entire Arabah Valley. The following year (1116), Baldwin went out on another campaign, and marched as far as Ayla on the coast of the Gulf, and built a fortress in Ayla to be able to control the land route for convoys between Egypt and the Levant, and Baldwin was able to build a fortress on Pharaoh's island located opposite Ayla in the Gulf of Aqaba. Thus, the Crusaders were able to oversee the Sinai Peninsula, which began to stir in their hearts memories and religious feelings dear to them, but despite this, the monks of St. Catherine's monastery refused to host Baldwin for fear of the Fatimids ' revenge in Cairo, which made Baldwin leave back to Jerusalem.
Baldwin continued his strategy aimed at controlling the Sinai Peninsula and the roads leading to it, so he built the Wadi Musa fortress in 1117, and the following year Baldwin went on a campaign through the Northern Road that passes through North Sinai, and reached Farma, where he stormed and burned it, and during his return he fell ill, as a result of eating a meal of fish that led to his death, and carried his body to Jerusalem to be buried. Al-Arish was attacked by the Crusaders in 577 Ah/ 1181 ad and the Sinai palm trees were cut down and the Crusaders carried their trunks to their country to be used in the manufacture of ships known as"Jalab", which are made of palm trunks, as part of the plan of Reynald of chateon, the governor of the Crusader fortress of Karak to control the Red Sea. However, Raynald's plan to control the Sinai and the Red Sea failed as a result of the efforts of the Ayyubids, especially Saladin, to stop Raynald's campaigns in the Red Sea, which reached as far as Aden, and Husam al-Din's Pearl fleet, which destroyed the Crusader fleet.
It is noteworthy that during that period, there was an increase in the evasion of caravans from paying fees and Customs, taking advantage of the turmoil caused by the Crusader presence in the Levant, so those caravans used the uninhibited trade routes between Egypt and the Levant, such as the "madriya" road, meaning dry mud, and it was named so because of its proximity to the Nile, they also used the "Badriya or faqan" roads away from the usual northern route to escape the threat of the Crusaders, and the caravans the ayyubis during the defeat of tell Safia in 573 Ah/1177 ad. The Ayyubid era was characterized by remarkable interest in the reconstruction of Sinai due to the conditions of the Crusades, which dictated the need to renovate castles and ports for fear of this imminent danger, Saladin rebuilt and repaired the port of tur in 580 Ah/1184 ad, the age of the boats and the port, and boats began to arrive loaded with goods from Yemen, and the owners of the in the Red Sea. Saladin was able to wrest the port of Eilat from the hands of the Crusaders in 566 Ah/1170 ad, and then the Red Sea came under his control. Also, at the end of the Ayyubid era, Saleh Najm al-Din Ayyub built the town of Salhiya in the "land of the sabakhs" (extension of the Bardawil Sabkha) in 644 Ah/ 1246 ad to be a stop on the road leading to the Levant.
Modern times
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Egypt began new events with the accession of Muhammad Ali to rule Egypt in 1805, the most important of which was his establishment of the Al-Arish governorate in 1810 within the administrative formations that he established in this year, which represented the first organized administrative form in Sinai in modern times, and has administrative competencies and boundaries, and put at the disposal of the governor of Al-Arish a military force to protect Egypt's eastern borders, and a regular force to protect security inside the city. It also established a customs point and a quarantine point (corinthina) in Al-Arish. As for tur, it was administratively subordinate to the Suez governorate, while Nakhl was included in the Hejaz castles administration, which followed the calendar pen in Egyptian Finance.
During the reign of Ismail (1863-1879), several events related to the Sinai took place, including the visits of many travelers to the Sinai, the most important of whom was Professor Palmer Palmer, who was sent by Britain in 1868 at the head of a scientific committee to explore the Tur region and draw a map of the Sinai. But the most important of those events that affected Sinai during that period was the opening of the Suez Canal for navigation in 1869, the creation of which had important effects on Sinai society, as we will see in the coming chapters. One of the results of the establishment of this important navigation corridor was the establishment of a number of cities on both banks of the canal, Ismailia was established almost in the middle of the canal, and a new city was established on the Arish road, namely the city of Al-Qantara.
In 1956, Israel, France and England launched an organized attack on Egypt in the so-called triple aggression against Egypt.the popular resistance carried out heroic actions to repel the Franks and the English. Israel took the Sinai completely, but a resolution was issued by the Security Council at that time to return all the occupied land to Egypt. illegality of the attack on Egypt. on June 5, 1967, Israel launched an attack on Egypt, Syria and Jordan and occupied Sinai, the Golan and the West Bank of Jordan. Despite the enormity of the loss, the Egyptian army was able to overcome this ordeal in its steadfastness against the Israeli forces and entered the war of attrition, at which time "Gamal Abdel Nasser" died in September 1970.
Mohamed Anwar Sadat took over the government after Gamal Abdel Nasser, worked to settle the internal problems of the state and prepare Egypt to fight a war to liberate the Sinai. On October 6, 1973 at two o'clock in the afternoon, the Egyptian Armed Forces and the Syrian Arab Armed Forces carried out an attack on Israeli troops in both the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan. The war on the Egyptian front began with the air strike launched by the Egyptian air force against the Israeli troops, the Egyptian troops crossed to the east bank and raised the Egyptian flag.
President Anwar Sadat entered into the settlement of the Arab-Israeli conflict to find an opportunity for lasting peace in the Middle East region, he approved the peace treaty submitted by Israel (Camp David) on March 26, 1979 with the participation of the United States after President Sadat's visit to Israel in 1977, and Israel withdrew from the Sinai Peninsula completely on April 25, 1982 with its withdrawal while retaining the Taba border strip and the Egyptian government recovered this strip later, based on the arbitration that took place in the International Court of Justice later.
Geography and population
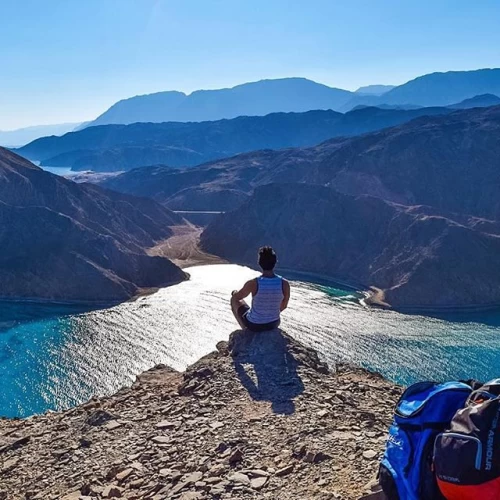
Sinai is a peninsula located west of Asia in the extreme northeast of Africa, between two latitude circles 44 27 South at Ras Mohammed, and 20 31 north at Tel Rafah on the Mediterranean coast, and between two meridians 18 32 west at the eastern shore of Lake alligator, and 54 34 East at Taba on the coast of the Gulf of Aqaba, with an area of about 60,088 km2, bordered to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, to the West by the Gulf of Suez and the Suez Canal, to the East by Israel and the Gaza Strip, the Gulf of Aqaba, and to the South by the Red Sea, which is considered a ring connecting the continents of Africa and Asia, Sinai is surrounded by water from most sides, as the Sinai Peninsula alone owns about 30% of the Egyptian coast, it is located between the Mediterranean Sea with a length of 120 km، The Suez Canal is 160 km long, the Gulf of Suez is 240 km long, and the Gulf of Aqaba is 150 km long.
Geology
The Sinai Peninsula is part of the area of the front platform of the great Arabian Shield, and the rocks of this shield appear in the south and a regional mile towards the north, where it is followed and covered by the sector of sedimentary rocks and the Sinai Peninsula is divided into three natural regions arranged as follows from North to South:
The plateaus of central Sinai
It is located north of the 30th parallel and extends from East Ismailia to Rafah along the Mediterranean Sea, and it is a large wavy plain that descends from the Teh plateau gradually to the Mediterranean Sea, and it is also a flat land with many valleys, eyes and tributaries that consist of rainwater. the northern Plains region in Sinai includes three sectors:
The coastal sector consists of shallow waters, and includes several swamps, lakes and wetlands, and these phenomena begin with the navigation of porfouad, which is located east of the Suez Canal, and then Lake Bardawil, which has a length of about 130 km, extending from Muhammadiyah east of Port Said by about 35 km west until before El Arish East by about 50 km, and Lake Bardawil is connected to the sea with a bugaz about 100 m wide, and in winter the entire lake consists of one body of water and then recedes from its eastern sector in summer to form two lakes it is located at Sheikh Zuweid between El Arish and Rafah, about 2 km from the Sea coast, surrounded by sand dunes and palm trees from the North and West.
The plains sector is located just after the coast line, and its maximum height is about 200 m.the area of these plains is 8000 km2. it widens a lot in the West at the Suez Canal and then narrows slightly in the Middle. these plains are a natural extension of the desert east of the Nile Delta. the most prominent features of this Plains range are the sand dunes scattered there and the sand dunes in the plains of North Sinai represent a natural rainwater reservoir, and they are mainly relied on in agriculture.
The domes sector is located directly south of the plains range and includes distinct groups of domed mountains, which consist of limestone, and its area is about 13 thousand km2 and the height of its base Plains is between 200 - 500 m above sea level, while mountain islands with heights ranging from 400 to 1000 m are spread over it, and between these heights there are mountain openings used as corridors and roads for transportation and movement, in addition to the spread of wells and springs, the most famous of these corridors are Metla pass, Capricorn pass, and these corridors end to Wadi Al-mleiz, heading northwest near Bir al-jafjafah, and when heading north, Jabal Al-Halal, Jabal al-maghara, which reaches a height of 400 to 700 M, and these mountains are interspersed with a group of valleys such as Wadi Al-Fath, Wadi Al-Mazraa, Wadi Al-Masjid, Wadi Al-maghara, Wadi al-aithli, Wadi al-Hasna, and Wadi Al-Malhi.
The territory of the plateaus in the center.
Wadi Ghazal
It is located between lines 30 and 29 and is located in the central Sinai region, which is a series of plateaus interspersed with some mountains that gradually slope towards the North, and also penetrate from south to North Wadi al-Arish and Nakhl point in the middle, and its height ranges from 500 to 1500 m above sea level, the most famous plateaus of this territory are the Teh plateau, which extends to about 140 km, then the ajma plateau, which is located to the north of the Teh plateau and extends for about 115 km, despite these general features of the the plateaus are in central Sinai, but it is possible to divide them into three sectors, the main of the western sectors, a mountainous sector is a group of mountain blocks interrupted by valleys, and the valleys of this sector are heading west.
The central sector is closer to a plateau, and the valleys of this part have a north-south direction and discharge in a north direction.
The eastern sector is less high and interspersed with valleys heading towards the East, the most famous of which is Wadi al-Arish, and it is about 250 km long.most of the Valley and its tributaries are located within the central Sinai region, which is the largest of the Sinai valleys, and the tributaries of Wadi al-Arish are multiple and branched, so many of the known Central and northern Sinai sites are located on one or more of these tributaries. perhaps the most prominent of these sites are Nakhl, Bir Jebel, Al-Hosn, Bir Ghada, al-thamad, Al-kuntila, Al-qusayma, and Al-Sabha on the eastern border.
The territory of the Highlands in the South
It is located south of line 29 and is the territory of the mountains, occupying the southern and narrowest third of the Sinai Peninsula, between the Gulf of Suez and Aqaba, and can be divided into three main sectors::
South Sinai mountains
The coast of the Gulf of Suez is bordered on the East by the South Sinai Mountains area and the elevations in this area vary from one side to the other, they are in the chest of the walls are almost flat areas to form a corridor north of the Wadi grandil area by about 25 km, and the elevations continue from Mount Hammam Pharaoh up to Abu zanima with a length of 4 km, and then begin to decline until the coastal area south of Abu Redis, the most important and longest valleys is Wadi Firan, which defines the dividing line between the ajma plateau in the North and the Tur mountain block in the south, thanks to its tributaries - especially Wadi Akhdar the Slav Valley and the Sheikh Valley - it goes straight to St. Catherine in the heart of the highest mountain forest of Sinai.
The coast of the Gulf of Aqaba starts from Ras Mohammed point in the south, and extends north to Taba, and the coastal area of the Gulf of Aqaba abounds with marinas and bays that drain into some valleys, as for the valleys of these two sectors of South Sinai, they are organized in a chain emanating from the heart of the mountain massif in the interior and most of them are heading to the Southwest, and some of them are heading directly to the West, and all of them drain into the Red Sea, then a group of smaller Valleys The Valleys in this area are a Monument Valley, which is the longest, and some of its numerous tributaries lead to the area of St. Catherine's monastery, while it pours It is at Dahab, and also Wadi Qani, which is a small valley close to the coast, and Wadi kid ends its main estuary north of Nabq Reserve, and Wadi Arbaeen.
In this mountainous area there is a forest of mountains of high altitude, the most prominent of which is Mount Catherine, which reaches a height of 2641 meters, followed by Mount Umm Shomer, which reaches a height of 2586 meters, Mount theB, Mount Moses, Mount Sabbagh, Mount Tarbush, Mount safsafa, Mount Bab al-Dunya, Mount tucked, Mount Banat, Mount Serabit Al-Khadim, and Mount gharab.
The Natural Life
The Sinai Peninsula contains a number of nature reserves that include many species of plants, animals and fish, the most prominent of which are Nabq Reserve, Ras Mohammed Reserve, St. Catherine Reserve, Taba Reserve, and Abu galum reserve, the Sinai ecosystem is a desert ecosystem and is a natural result of climate and soil factors, so the percentage of vegetative cover almost disappears in some arid areas, while it increases somewhat in many patches so that it ranges between 1 - 4 %, especially in the northern coastal dunes, which are not devoid of vegetation patches that help to stabilize them. the types of plants and herbs prevailing in Sinai range from dry species, salty species found in swamps, to wet species found in high mountainous areas and on mountain slopes, peaks and valleys, but in open plains it seems a wooded area rather than a desert, where shrubs and trees thicken, especially from Ethel and Acacia.
Palm and castor trees are one of the most important plant elements adapted to the coastal sandy environment, which is proved by the salty Acacia and eucalyptus trees, while lichens cover the rocks of the coastal highlands by 90% due to the high percentage of dew, although the percentage of precipitation does not exceed 90 mm in some areas, and the Highlands are topped by lavender or lavender plants, thyme, astragalus, ephedra, daffodils, tulips, and Phoenician juniper trees. the tahe plateau region is dominated by Arabian desert plants, which are rare on bare rocks, and the vegetation cover increases at the bottom of the valleys, where the cockroach, thamam and Sala are common, in addition to the following plant species: In the Sinai mountains, the vegetation cover is becoming denser and more diverse, with Hawthorn, Syrian lichen and green cypress, figs, Sycamore and quince spreading.
As for the animals, there are many species on the peninsula, such as Wart, Egyptian hyena, striped hyena, coyote, hedgehog of all kinds, porcupine, Tigers, Egyptian mongoose, Arabian oryx, Nubian ibex, domestic Ram, funk, hug the Earth, Lynx, hares, Dorcas gazelle, mice and Springboks, and the most important birds that have been recorded on the peninsula are Pelicans, greater flamingo, small white heron, chicken marzah, Stork, herds herds egrets, Hawks, quails, bitterns, white stork, lark, lark-Heron, jokes, and pheasants are fierce. many fish and marine plants have also been recorded on the coasts of the Sinai Peninsula, the most important of which are clown fish, fish Picasso butterfly fish, dolphins, sea anchovies, Sharks, shrimp, sea cucumbers, some species of jellyfish, squid, octopus, moray eels, topless gills, pufferfish, and Spanish dancer fish, mangroves, sea anemones, as well as multiple types of corals, the government has banned fishing in South Sinai to protect its marine life.